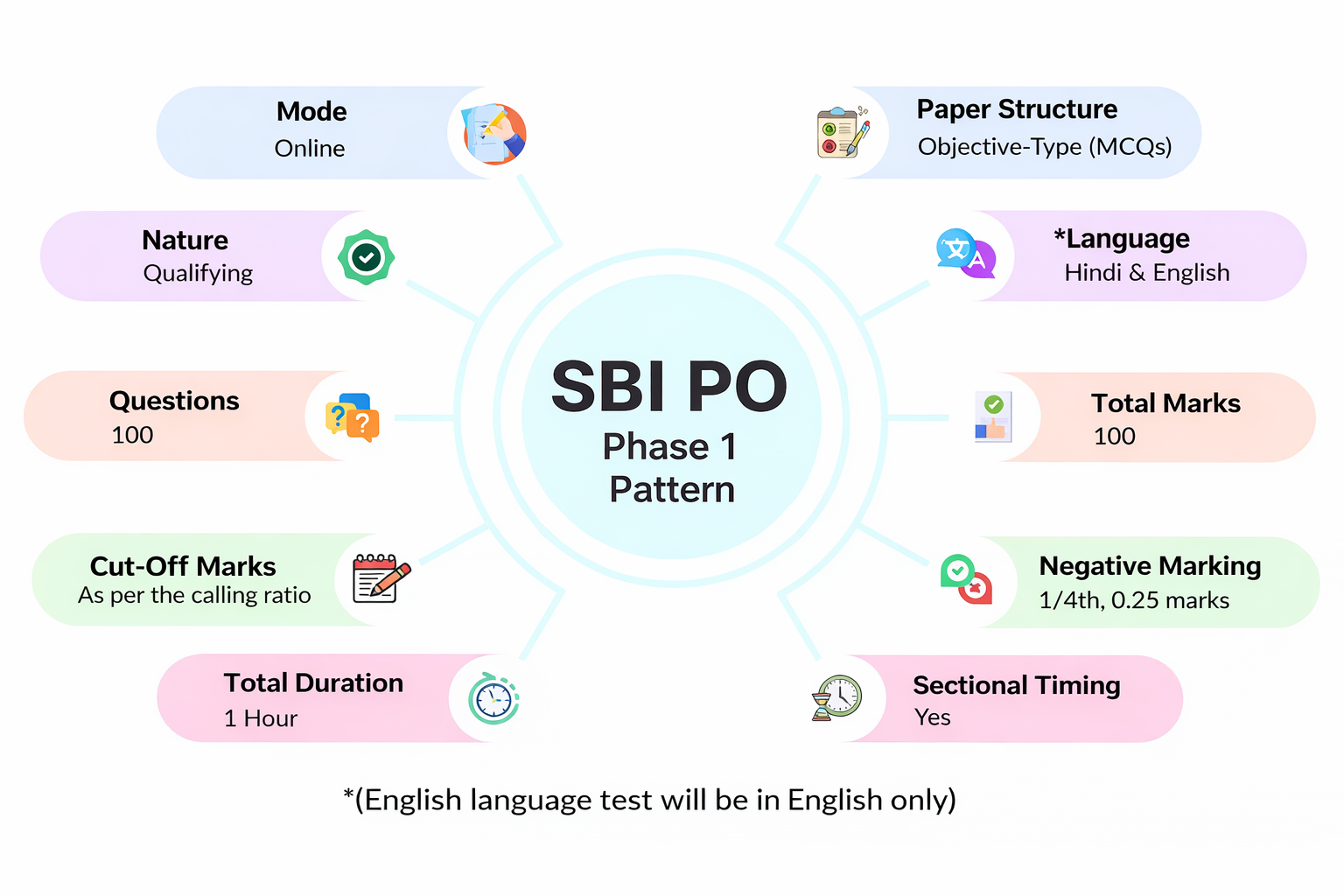
Introduction to Management is a foundational subject for UGC NET Paper 2 in Management and Human Resource Management. It explores the principles, functions, and practices of managing organisations effectively. The study material covers topics such as planning, organising, staffing, directing, and controlling, along with leadership, motivation, and decision-making processes. It helps candidates understand how managers coordinate resources, achieve organisational goals, and respond to dynamic business environments. With a focus on both theory and practical applications, this material equips aspirants with essential knowledge to analyse management challenges, develop strategic solutions, and perform effectively in managerial roles.
Meaning and Definition of Management
- Management is the process of designing and maintaining an environment in which individuals working together in groups efficiently accomplish selected aims.
- Marry Parker Follet: She says “Management is the art of getting things done through others. This definition lacks planning and organisational aspect but it provides that management and organisation is different thing”.
- 3. George R. Terry: He defines “Management as a process of planning, organizing, actuating and controlling perform to determine and accomplish the objectives by the use of people and resources”.
- Henry Fayol gave the following determination of management in his book, “Industrial and General Administration”. “To manage is to forecast and to plan, to organize, to command, to coordinate and to control”.
- Peter Drucker defined management in his “The Principles of Management’ “Management is a multipurpose organ that manages business and manages managers and manages workers and work”.
- As per modern view “optimal utilization of available resource is management”.
Nature of Management
-
Management as Multi-Disciplinary:
Although management is altogether a separate discipline but it draws knowledge and concepts from various disciplines such as psychology, sociology, economics, anthropologies, ecology etc. Management integrates the ideas, knowledge, skills and concepts from various disciplines and presents newer innovative concepts which can be put into practice for effective management in the organisation.
-
Management Principles are Relative not Absolute:
Management principles are applied keeping in view the time, place, socio-culture factors, individuals working in the organisation, nature of organisation itself and other environmental as well as economic conditions. Therefore, some principles cannot be applied everywhere and nature of management principles is not absolute, but relative.
-
Management as a Science or an Art:
Management is considered as Science because of the following features:
i. There is logical consistency
ii. There is systematic explanation of activities
iii. There is critical evaluation of all aspects
iv. There is experimental analysis of all statements
v. There is logical formulation of problems.
vi. There is obvious deduction of specific hypothesis
viii. There is testing of every theorem.
ix. There is logical illustration of every concept
x. There is empirical confirmation of every theorem.
There is continuous advancement through knowledge. There is proper prod prediction, definition measurement and confirmation of all concepts like science But principles of management are not as strict as the principles of science. They cultural and social difference. That’s why management is referred as an applied scienc subject to change while applying in different organisation and different locations, because rather than a pure science.
Management is considered as an Art because of the following features
A distinct way of representing something is called art. It involves creativity in order make the things more effective. Since every manager has their own style to perfon managerial activities so we can say that if is an art.
There is application of skills, concepts, theorems, principles and normal are enough. There is an ardent need of creativity and art in the hands of managers. There is need of experience and practice to get excellence.
-
Management as Profession:
Management is considered as profession on following ground:
i. There is need to acquire a particular knowledge, to become good manager just like other professions as doctors and engineers.
ii. There are specific ethical codes for management profession like other professions of doctors, advocates etc.
iii. There are special and specific motives of this profession for the society.
-
Management in Universal:
i. Management principles are inevitable and necessary for all kinds of organisations.
ii. Management principles are all pervasive and therefore applicable to all the levels of management as well as all the departments.
-
Management is Goal Oriented:
Management is a means to achieve certain goals which are termed as organisationa goals.
i. There goals are achieved with the utilization of all available resources.
ii. The management will be purposeful and surcesend only if the group goals o organisational goals are accomplished
-
Management as Dynamic Process:
The management process can be changed depending on nature of problem. A single format cannot be suitable for all the situation. So the manager should adopt the variations in managerial activities
Importance of Management
- Effective Utilisation of Resources:
i. Management is to make optimum utilization of all the available resources.
ii. Management helps in creating and maintaining an environment conductive to highest productivity,
- To Incorporate Innovations:
Management is not only science but an art also and therefore creates new ideas, new concepts, new products and new methods to improve the efficiency and achieve excellence.
- Integrating Various Team Groups:
i. Management is to integrate various individuals to work efficiently so that the group can realize its objectives.
ii. Management looks for mutual cooperation and coordination among all groups members.
iii. Management is to reconcile the objectives of the group with those of its members so that each one is motivated and starts working towards accomplishing the objectives.
Minimisation of Cost:
- In this cut throat competition it is every important to minimize the cost to allure the customer for the sustainable survival.
- Management plays an important role in reducing costs and improving efficiency and thus enabling the enterprise to be competent to face competitions and earn profits.
Provide Competitive Advantages
- To succeed in a particular market a company must do something better than other companies in that business. That something may be only one aspect of the product service as long as customers value it high.
Levels of Skills and Management
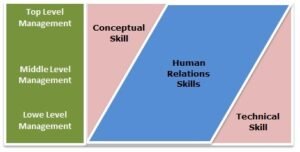
Levels of Management:
Broadly management can be divided into three levels namely Top level management, middle level management and low level management.
-
Top Level Management:
Top level management is generally occupied by the ownership group. It is highest level in the managerial hierarchy. It consists of Chairpersons, Board of Directors, CEO & other higher authorities. The functions of top level management can be stated in following points:
i. Top level is concerned to determining primary objectives, formulating basic policies, making vital decisions, controlling and coordinating activities of personnel.
ii. To decide corporate goals.
iii. To decide structure of organisation, creating various positions in organisation.
iii. Top level management perform the function of making plans, deciding corporate goa creating various positions, coordinating various sub-systems and liaisoning with outs parties.
2 Middle Level Management:
i. It consists of departmental managers, deputym formand administrative officers, etc. Middle level managers are the link between top level and lower level managers.
ii. Their main function is to prepare departmental plan, establish departemental goste, perform other managerial functions, explain and interpret policy decisions on their subordinates
-
Low Level Management:
It is also known as supervisory management. Low level management constitutes factory supervisors, superintendents, foreman, sales supervisors, etc. The main functions of Low Level Management –
- Planning of day-to-day work.
- Assignment of jobs and issuing orders and instructions.
- Evaluating operating performance.
- Sending reports and statement to higher authorities.
- Their main function is to guide and control the performance and rank and file workers and instruct them for day-to-day activities.
Skills of Management/ Managerial Skills(Robert Kurtz):
Several skills are required to successfully manage a large organisati environment. Some of the required skills are given below:

- Technical Skills:
i. They refer to the ability and knowledge in using the equipments, techniques and procedures involved in performing various managerial tasks.
ii. They require specialized knowledge and proficiency in handling a particular job.
iii. The manager must know about the kind of skills required to execute a particular job and about the kind of potential needed to acquire it.
2. Human Skill:
i. It refer, to the ability to work effectively with other people both as individual and a group.
ii. It reflected in the way the managers perceive their superiors, subordinates and peers.
iii. If technical skills involve mastery of ‘things, then human skills are concerned with understanding of people.
- Conceptual Skills:
i. They refer, to the ability to see the whole organisation and the interrelation between its parts.
ⅱ. They consider the ability to viz the entire picture or to consider a situation in totality.
iii. They also include the competence to understand a problem and trigger the mind find out its solution; which helps in decision making.
iv. To conclude technical skills deal with jobs, human skills with persons and conceptual skills with idea. It is necessary to have comprehensive package of all three for an efficient leader.
v. Thus, technical skills deal with jobs, human skills with persons and conceptual skills and ideas.
Functions of Management:
Basically, there are five important functions of management, which are as follows:
- Planning
- Organising
- Staffing
- Directing
- Controlling
Most widely accepted five managerial function given by Koontz O’ Done
(i) Planning,
(ii) Organising,
(iii) Staffing,
(iv) Directing,
(v) Controlling
Luther Gullick – POSDCORB:
P – Planning
O-Organising
S – Staffing
D – Directing
Co-Coordinating
R – Reporting
B-Budgeting